Excel Function: XLOOKUP
The Excel function XLOOKUP searches for a value in a table and then returns the corresponding value (at the same position) in a second table.
This function is typically used to search for a value in one column of a table and return the corresponding value from another column.
The XLOOKUP function is much more functional than the VLOOKUP function which only searches for the value in the first column of a table, and it's simpler to use than the combination INDEX + MATCH which requires using 2 functions.
Usage:
=XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array)
or
=XLOOKUP(lookup_value, lookup_array, return_array, if_not_found, match_mode, search_mode)
Example of Use
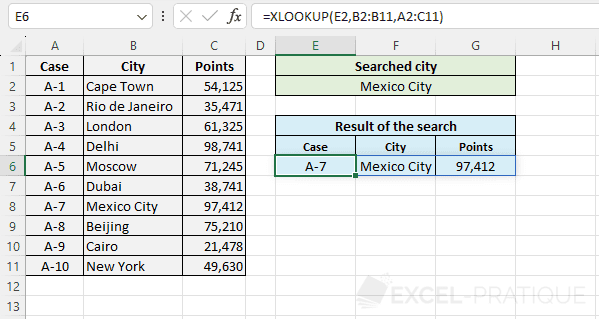
The objective here is to search for information based on the city name. The user should be able to enter the city name in the green part and then see the result of his search in the blue part:
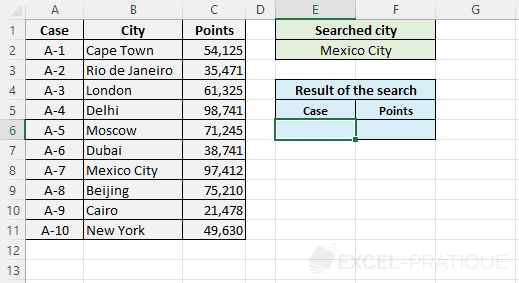
For now, it's the same example as the one on the INDEX + MATCH functions page, but this time, realized using the sole XLOOKUP function.
Select the XLOOKUP function and enter:
- Lookup_value: the value to search for in the table (here, the city name)
- Lookup_array: the table where the value should be searched (here, the cities column)
- Return_array: the table that contains the result to be returned by the function (here, the case numbers column)
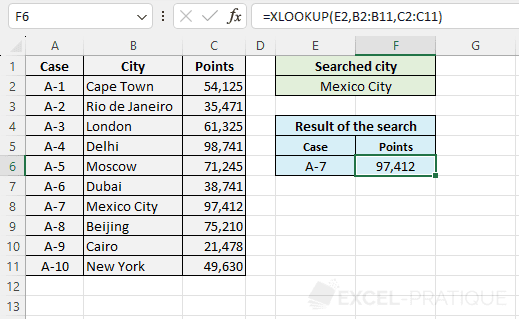
=XLOOKUP(E2,B2:B11,A2:A11)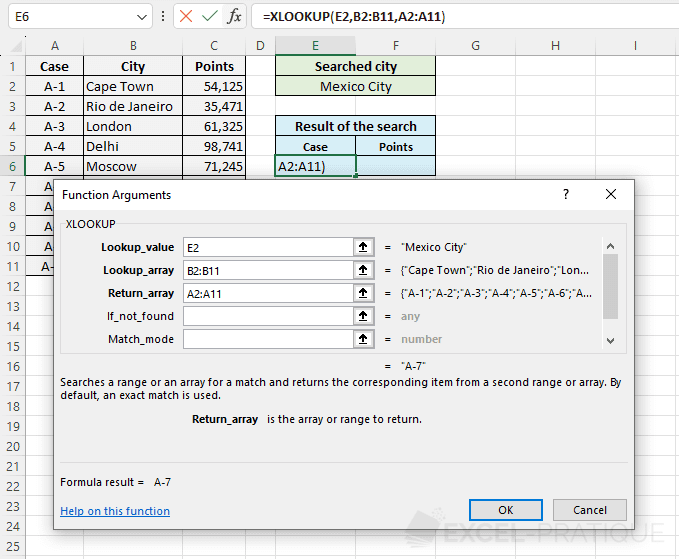
The case number is then displayed:
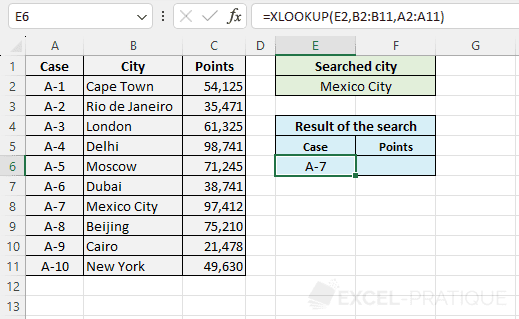
To then display the points, you just need to copy the formula and modify Return_array:
Optional Arguments
In the previous example, only the 3 mandatory arguments were entered in the XLOOKUP function, but there are 3 more that are optional.
The most useful is certainly If_not_found which allows you to specify the value to return if there is no result and thus avoid the #N/A error.
For example:
=XLOOKUP(E2,B2:B11,A2:A11,"-")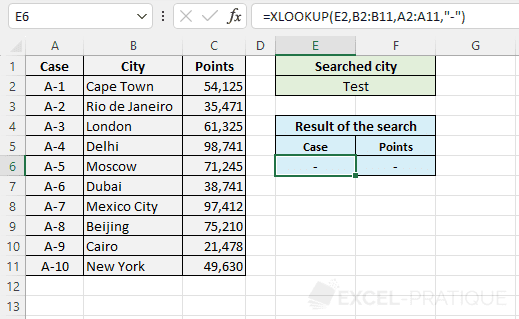
The second optional argument Match_mode allows you to choose the search mode although most of the time, you will only use the default mode (0):
- 0: exact match (if no match: an #N/A error or the If_not_found value)
- -1: exact match (if no match: the next lower value)
- 1: exact match (if no match: the next higher value)
- 2: wildcard match (where * replaces no, one or several characters, ? replaces one character and ~ allows to escape one of these 3 characters *?~)
For example, with mode 2 and search M* (or m*), the function will search for the first city whose name begins with M:
=XLOOKUP(E2,B2:B11,A2:A11,"-",2)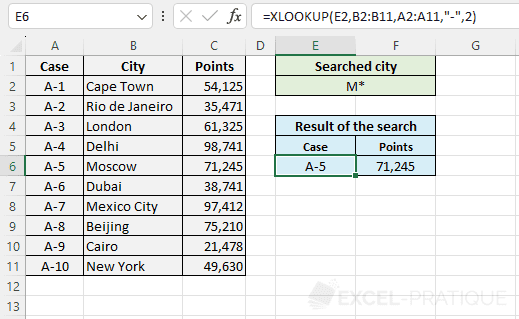
And finally, the last optional argument is Search_mode:
- 1: search starting from the beginning (by default)
- -1: search starting from the end
- 2: binary search ascending
- -2: binary search descending
Multiple Values
It is possible to return several values at once with a single XLOOKUP function.
For example, to return the entire line, enter the entire table in Return_array:
=XLOOKUP(E2,B2:B11,A2:C11)